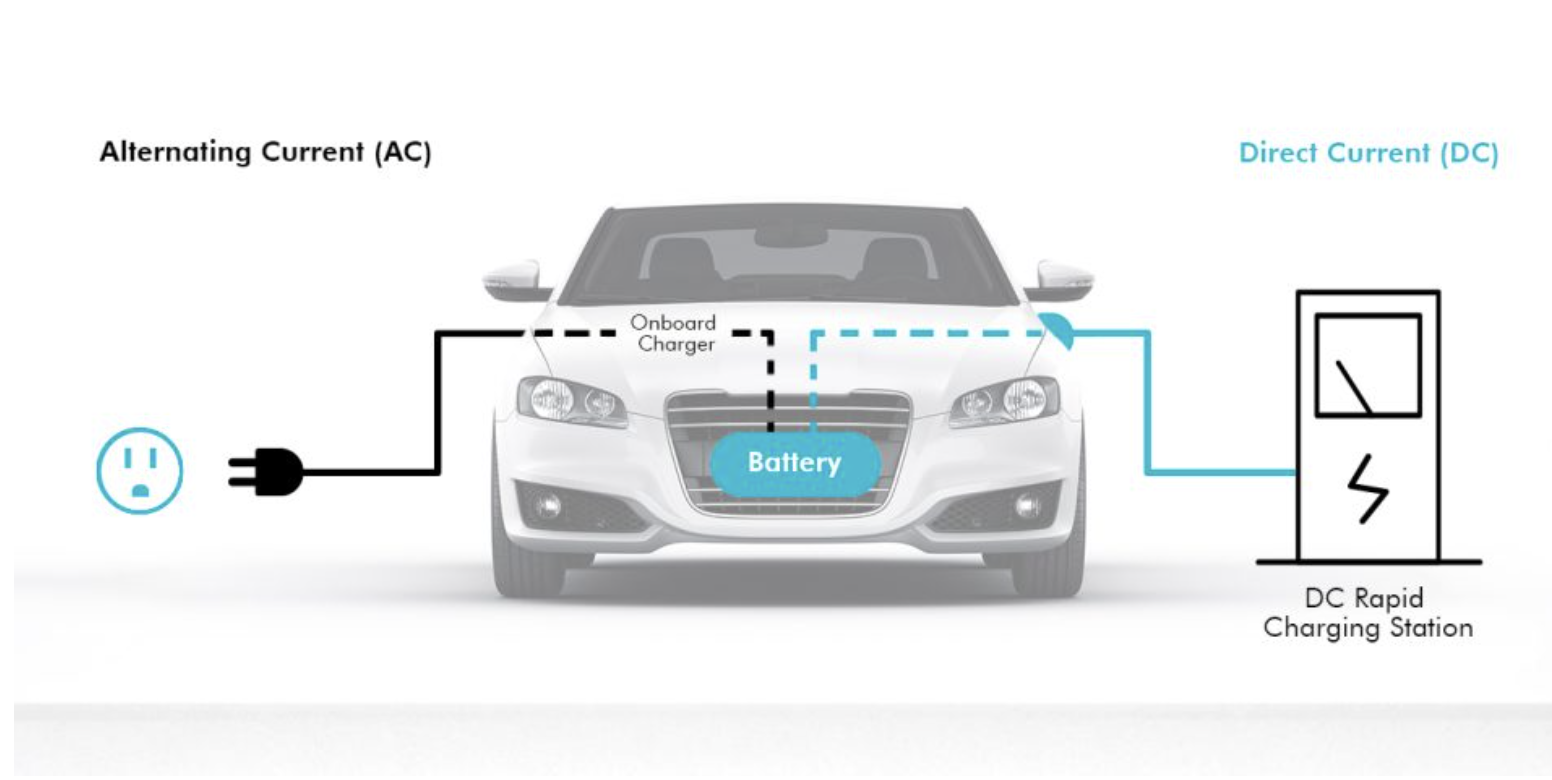
Do you know an important fact to consider for charging speed is the charging current? There are two ways to charge EV batteries: AC (alternative current) charging and DC (Direct current) charging. In this article, we break down the differences between AC and DC charging and the Pros and Cons for each.
AC Power VS DC Power Charging
Nowadays, the grid only gives AC power. However, the batteries in our EVs are only compatible with DC power. For electric vehicles, there is a built-in converter called the”on-board charger”. which converts AC to DC before the battery is powered. Moreover, AC Charging stations are used mainly with 7.6kW to 11kW because AC charging is capped by the on-board charger’s capacity, which is common at 9.6kW or 11kW. This is the most common charging method for EVs, especially for overnight charging or residential use.
Unlike AC chargers, a DC charger has a converter inside the charger itself, which means DC power is given directly to the battery without the on-board charger. DC can supply charging speed at a range of up to 100 km or more per hour. With the increased number of EVs, the number of public charging stations has also increased. You can easily find public DC charging stations in commercial or service stations on highways which allows you to charge your car within 45 minutes.
AC Charger Pros & Cons
Pros
- One of the biggest advantages of AC chargers is that they are affordable, and lower installation & maintenance costs.
- AC Chargers can be designed with portability features. You can simply plug it into a standard outlet wherever you are.
- Most AC chargers allow you to charge at a continuous or cheaper rate with a scheduler from a smart APP.
Cons
- Compared to DC chargers, AC Chargers are much slower and need 4-17 hours to fully charge your car.
- They are compatible with limited power because AC power depends on the capacity of the on-board charger.
- AC charger is also limited to your home panel capacity
DC Charger Pros & Cons
Pros
- Obviously, DC chargers offer the fastest charging speed and can charge your EV battery from 0-80% within 45 minutes.
- Allows you to charge more cars in a day since the charging speed is more efficient than AC Chargers.
Cons
- The purchasing, installation, and maintenance fees are expensive
- DC chargers need more space with limited locations.
- DC chargers need a large power supply which can be a challenge to local grid capacity.
In conclusion, DC and AC charging both are used and can be regarded as complements of each other. With better home AC EV chargers and increased DC charging infrastructure, we can increase the adoption rate of EVs while leaving range anxiety in the past.